(Hands-On) Create a Notebook Server in Kubeflow Cluster
The following video is an excerpt from a live session dedicated to reviewing the Jupyter notebook that makes up the solution for this particular Kaggle competition example.
After watching this video you will deploy a notebook server where you will use a Jupyter notebook to create a model for Titanic Disaster Survivor Prediction.
1. Check your Enterprise Kubeflow version
To check your version, refer to the bottom left corner in the Central Dashboard:
Remember your Enterprise Kubeflow version, as you will need to follow instructions that are specific to the version you are running.
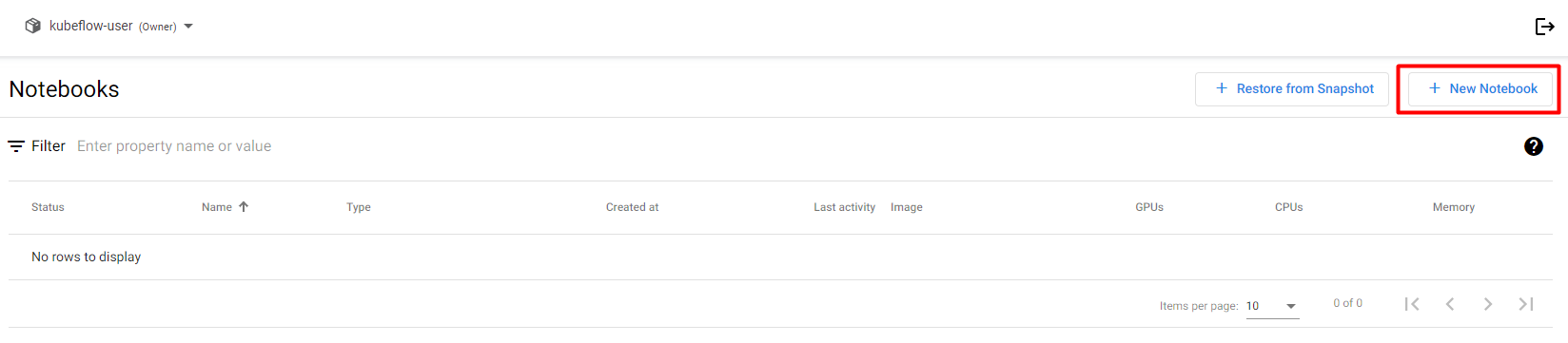
3. Create a new notebook
Click on + New Notebook:
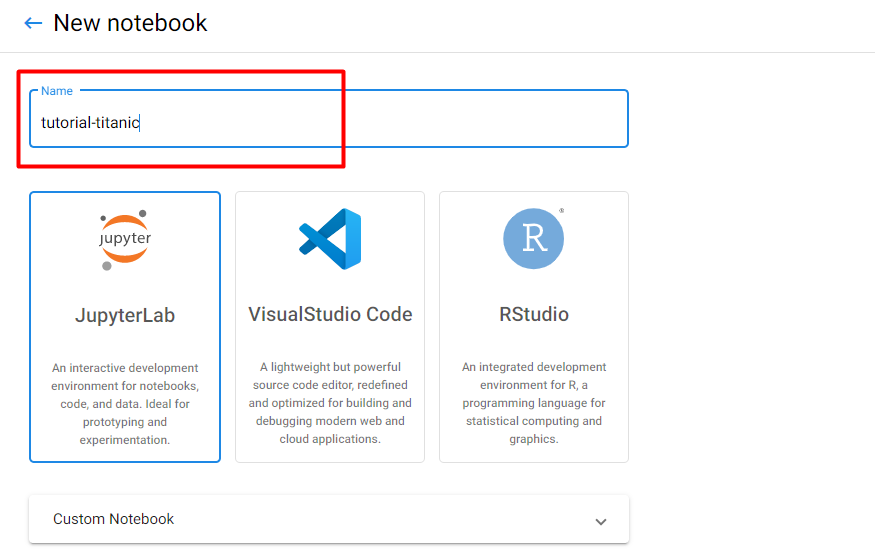
4. Name your notebook
Specify a name for your notebook:
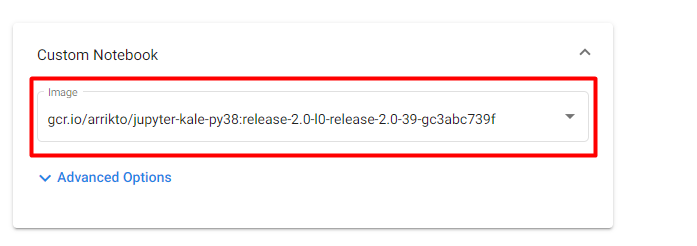
5. Select Docker image
Make sure you are using the default Docker image. This image will have the following naming scheme:
gcr.io/arrikto/jupyter-kale-py38:<IMAGE_TAG>
gcr.io/arrikto/jupyter-kale-py36:<IMAGE_TAG>
6. Add new data volume
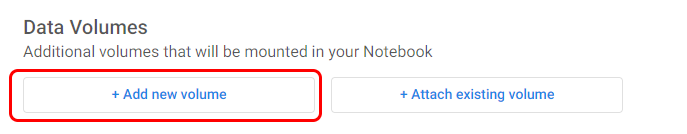
Select +Add new volume:
In Data Volumes choose:
- Type: Empty volume
- Name: data
- Size: 5 Gi
- Storage class: default
- Access mode: ReadWriteOnce
It’s important to name your new volume data, as in later steps you will run commands that refer to this name.
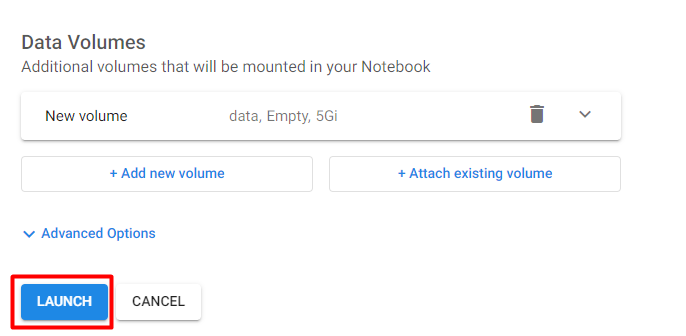
7. Create your notebook
Click LAUNCH to create the notebook:
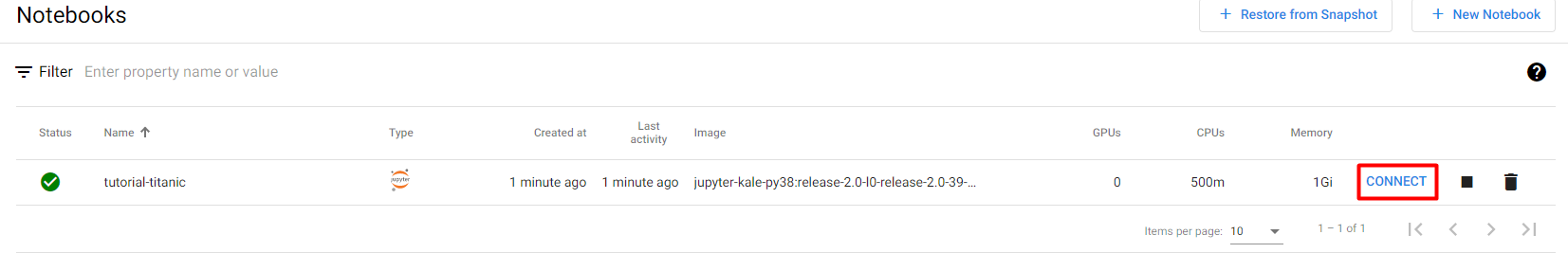
8. Connect to your notebook
When the notebook is available, click CONNECT to connect to it: