(Hands-On) Restore Notebook from a Pipeline Step
Now that you have run a hyperparameter optimization on your model, you probably want to take the best model and serve it. We are going to use KServe, Kubeflow’s component for serving models to production.
We are going to select the best trial of the Katib experiment and restore a notebook out of a snapshot of this pipeline run. We will use Rok to restore the notebook and we will have the model directly in the notebook’s memory. Then, we will use an intuitive Kale API to serve this model, without having to create any Docker images or submit new CRs. Kale makes this whole process seamless.
1. Restore notebook
Choose one of the following options based on your version.
a. Go to Snapshots tab
You are already on the best pipeline run, so click on the model_evaluation step and then go to the Snapshots tab. This is where you see the pipeline artifacts that Kale produced:
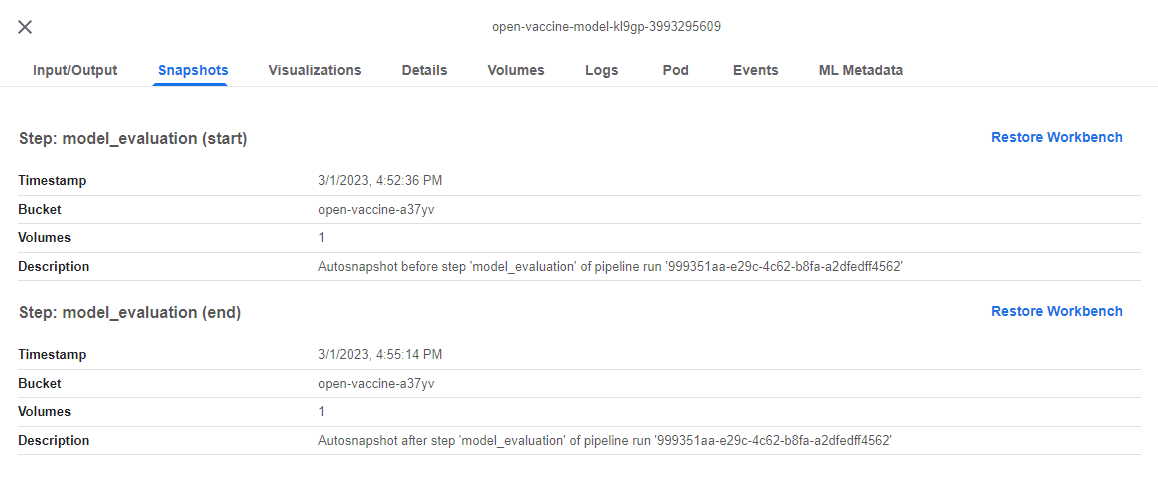
b. Restore state from pipeline
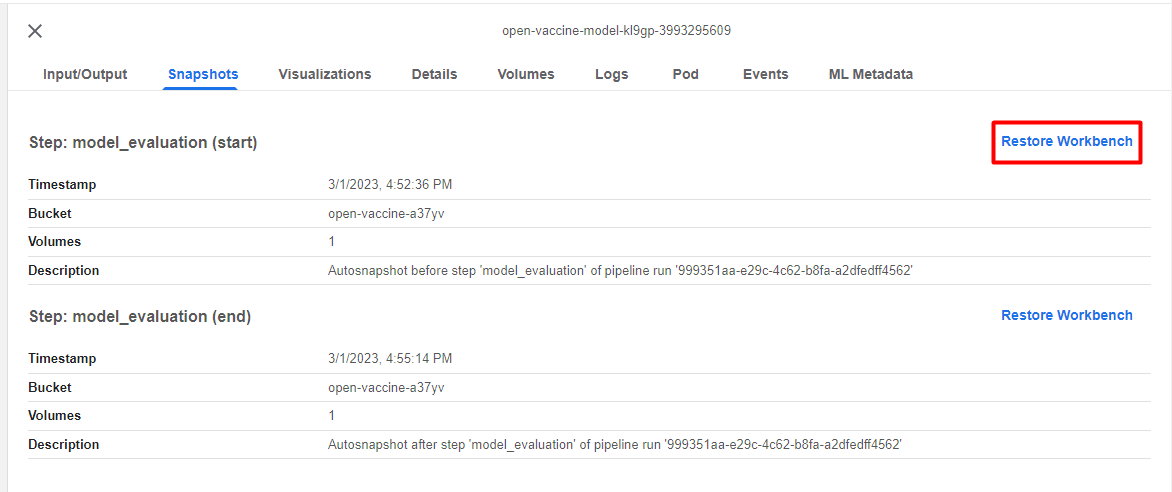
The first artifact is a Rok snapshot taken just before the execution of the model_evaluation step. Click on Restore Workbench to restore the state of the pipeline before the execution of this pipeline step:
a. Go to Visualizations tab
You are already on the best pipeline run, so click on the model_evaluation step and then go to the Visualizations tab. This is where you see the pipeline artifacts that Kale produced:
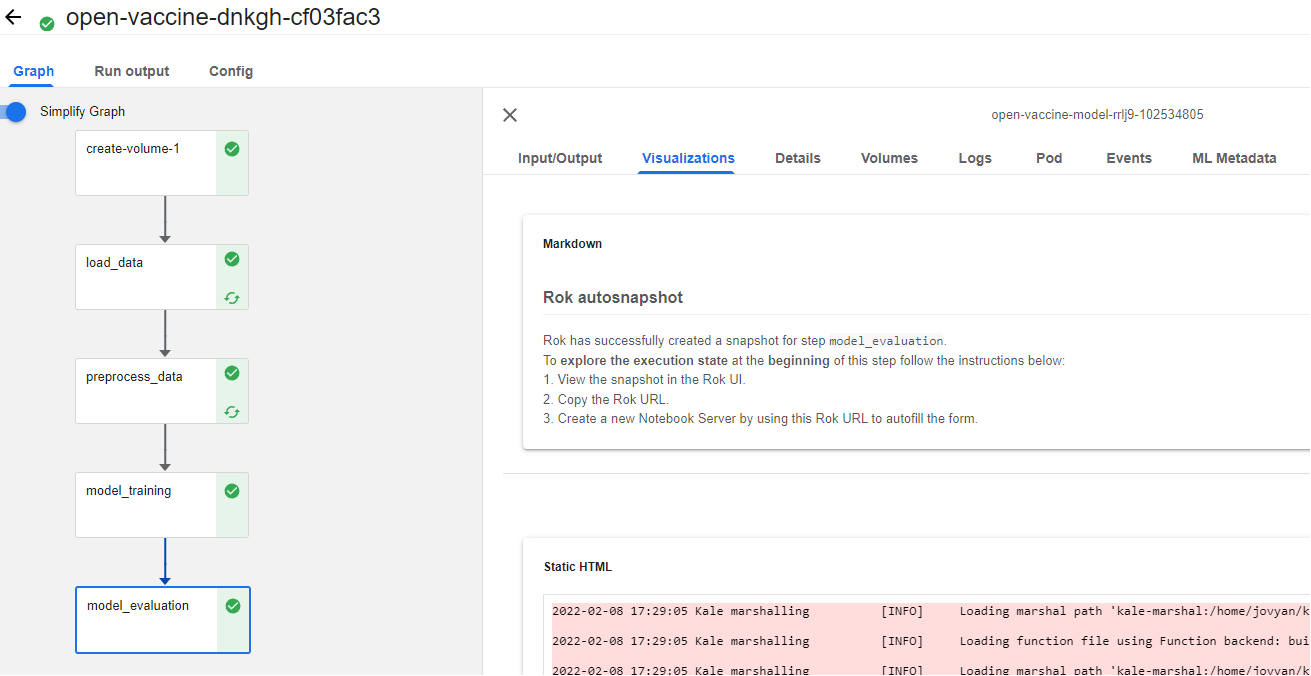
b. View the snapshot in the Rok UI
The first artifact is a Rok snapshot taken just before the execution of the model_evaluation step. Click on the corresponding link to view the snapshot in the Rok UI:
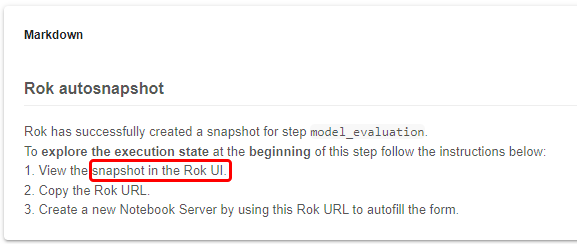
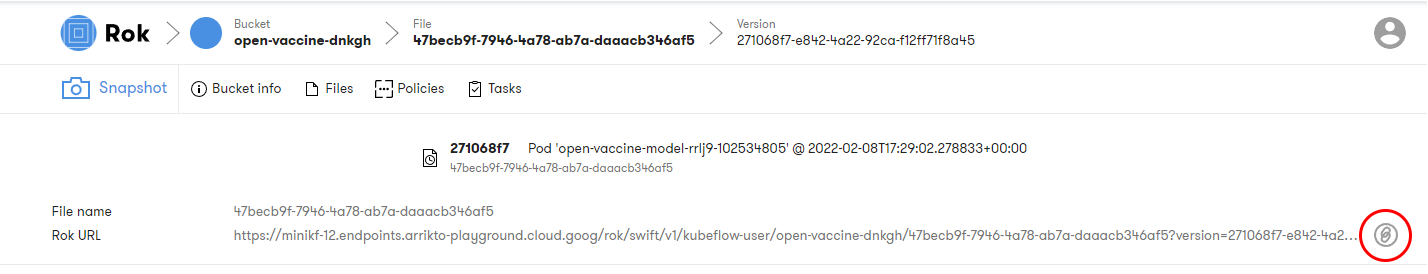
c. Copy the URL
Copy the Rok snapshot URL:
d. Go to Notebooks
Navigate to the Notebooks tab:
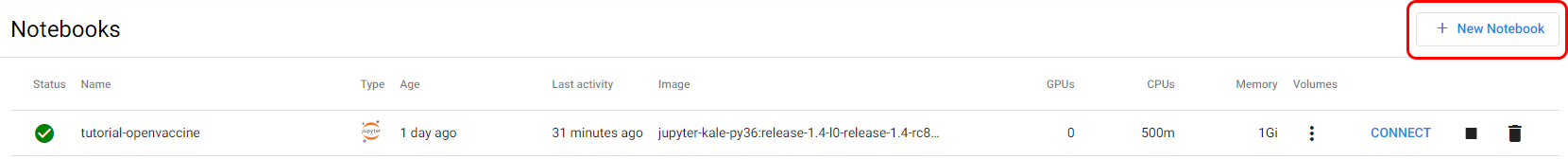
e. Create new notebook
Click on + New Notebook:
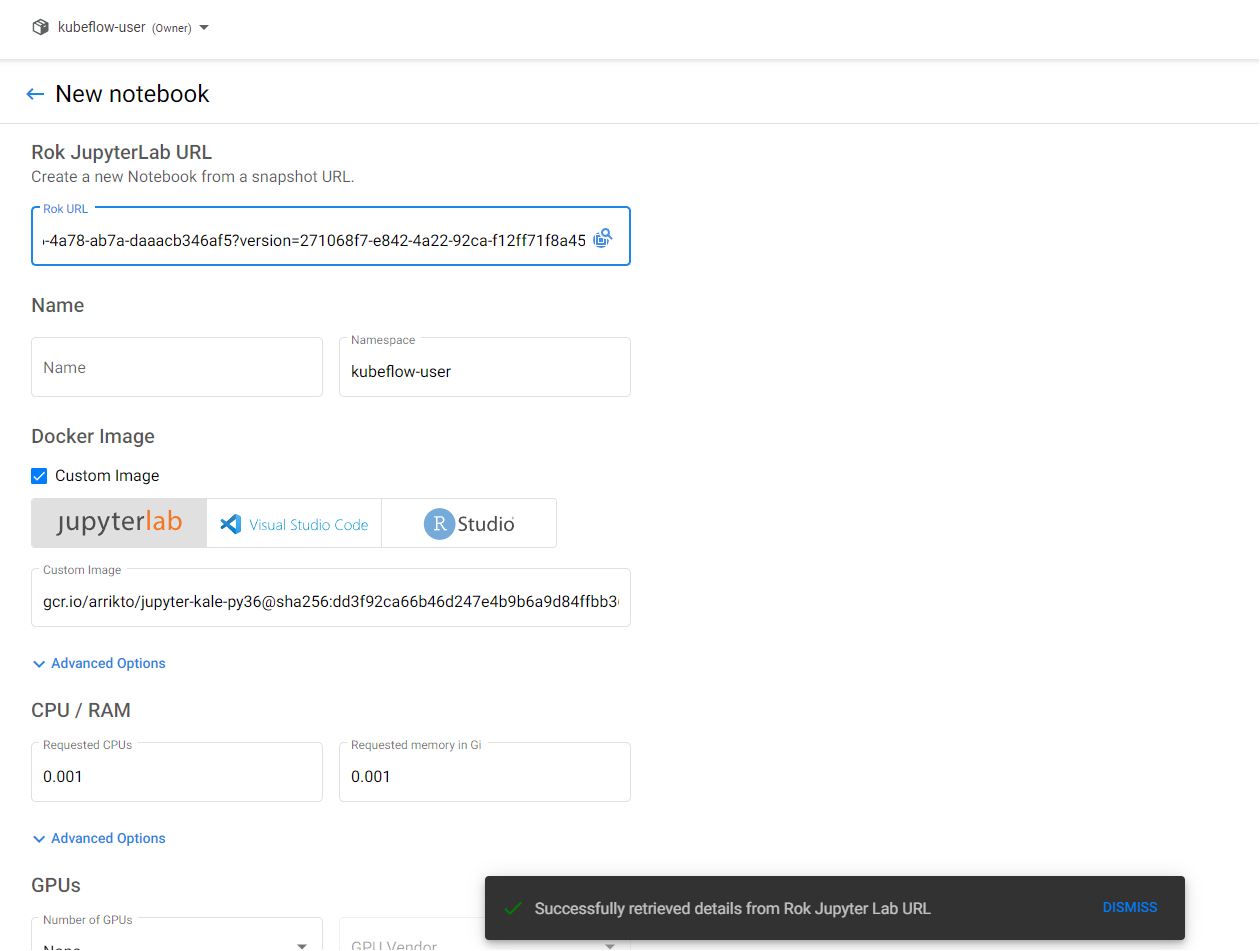
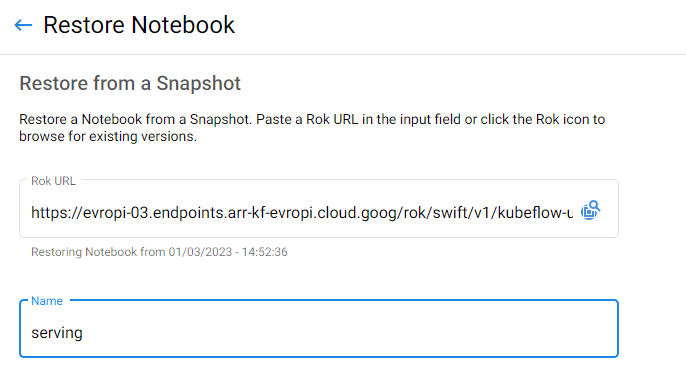
f. Paste the Rok URL
Paste the Rok URL you copied previously. The notebook info will be autofilled.
2. Name your notebook
Specify a name for your notebook:
3. Create your notebook
Click LAUNCH to create the notebook:
4. Connect to your notebook
When the notebook server is available, click CONNECT to connect to it.

In the background, Kale resumes the notebook’s state by importing all the libraries and loading the variables from the previous steps.
When you click on CONNECT and the new Jupyter tab opens, wait for a few seconds until you see a pop up saying that Kale has completely restored the notebook.