(Hands-On) Serve the Model from Inside the Notebook
The following video is an excerpt from a live session dedicated to reviewing the Jupyter notebook that makes up the solution for this particular Kaggle Challenge example.
After watching this video you will deploy an Inference Service to serve the model you create for the Kaggle Corona Hack Challenge.
In this section, we will restore the trained model from a Rok snapshot and evaluate it on the test dataset.
Choose one of the following options based on your version.
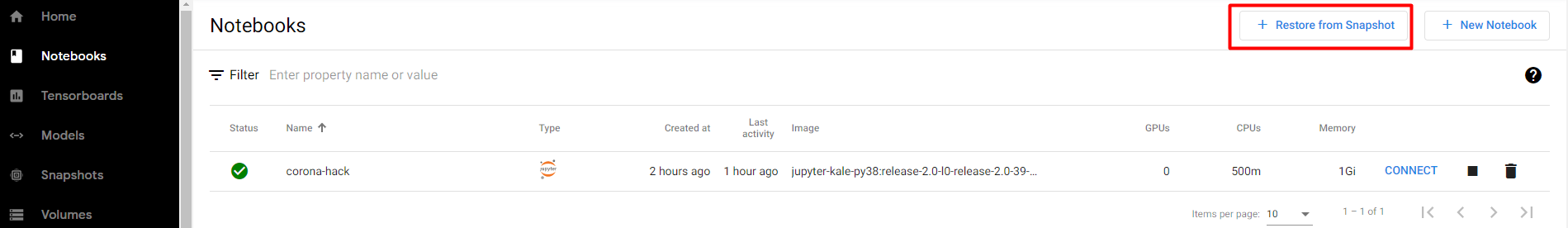
1. Go to Notebooks
Click on the Notebooks tab:
2. Restore from Snapshot
Click on the Restore from Snapshot button:
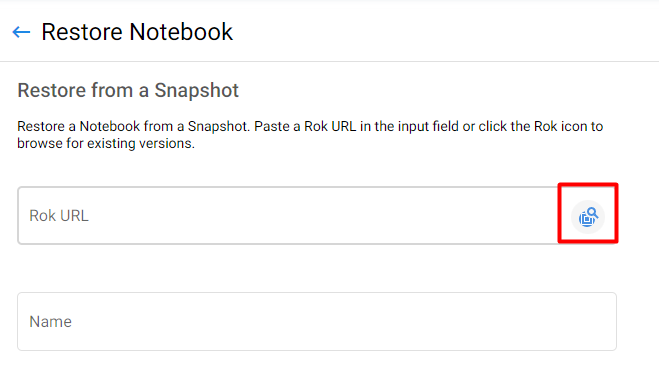
3. Search Rok snapshot
Click on the search icon to select the snapshot.
4. Choose the snapshot
Click on the artifacts bucket in the pop-up window:
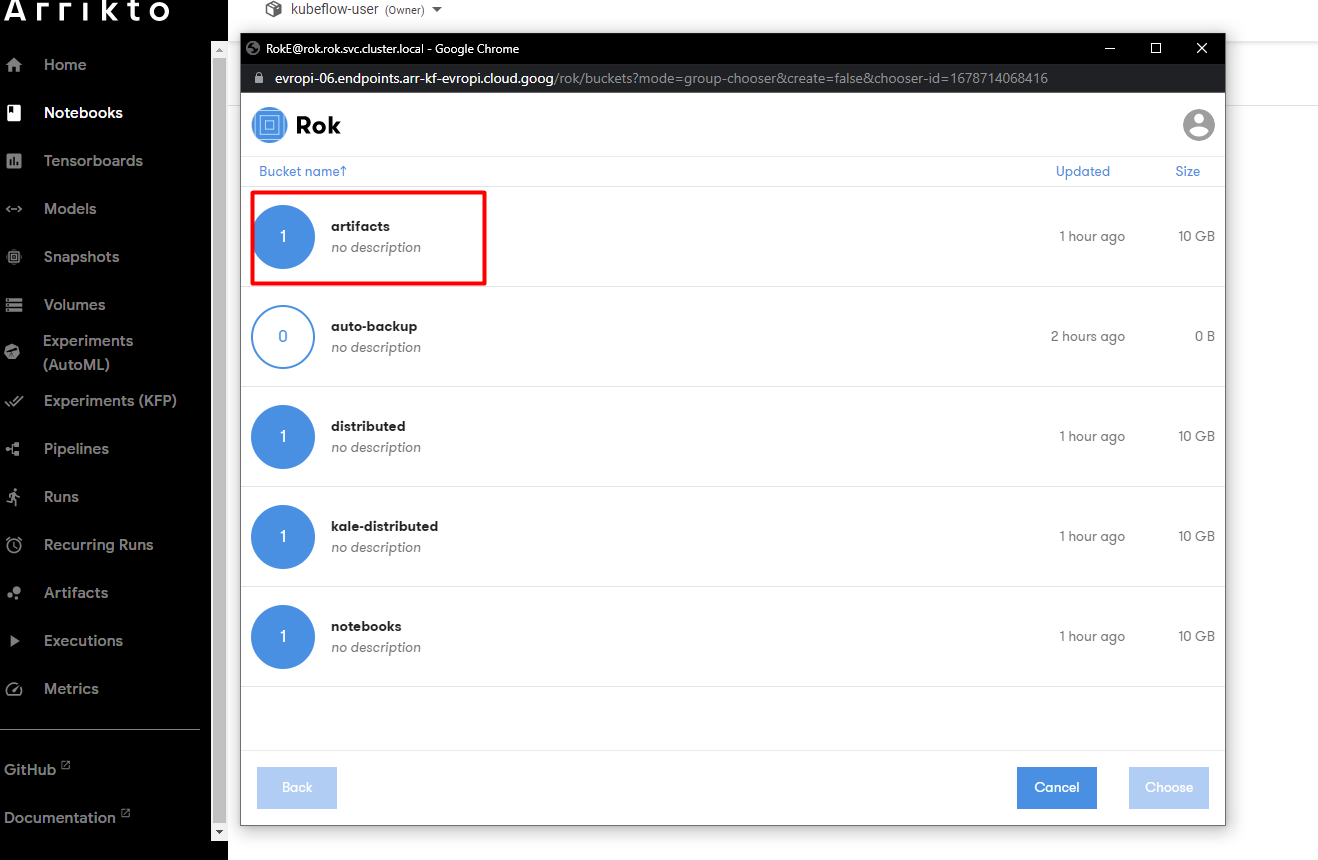
There should be one entry inside it. If not, select the most recent one based on the Created column, and click Choose.
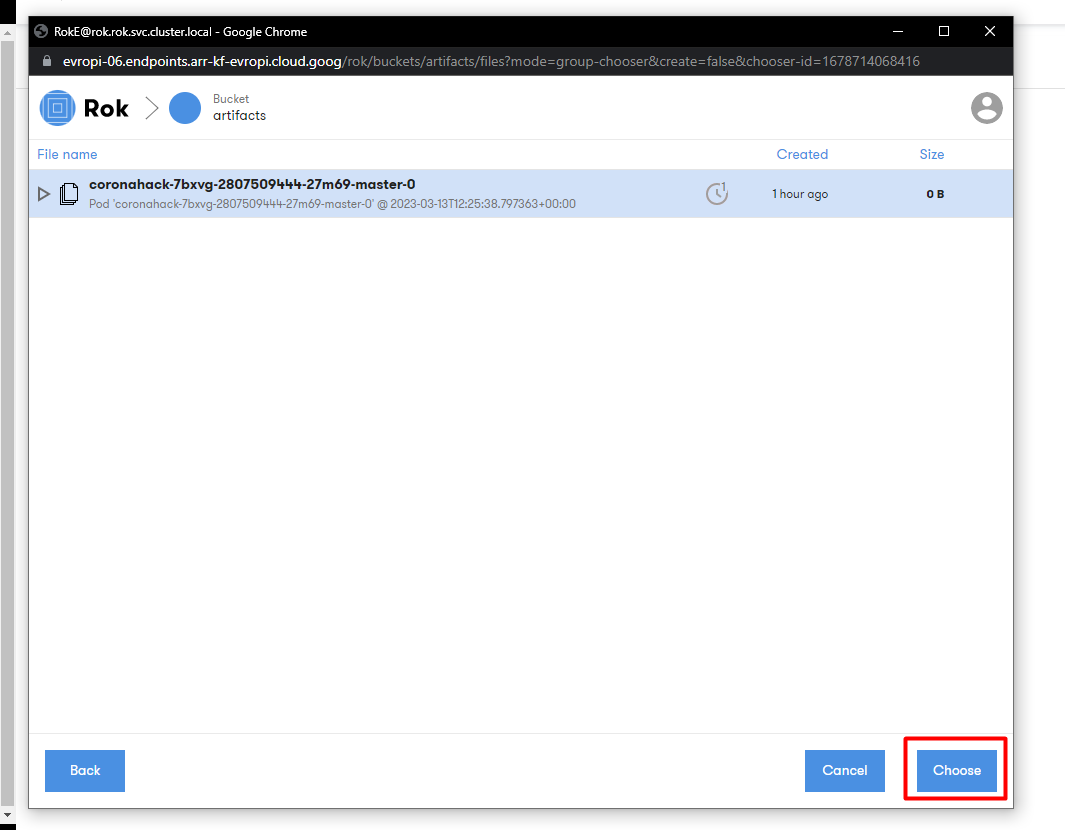
The Rok snapshot URL and the volume information should be retrieved automatically.
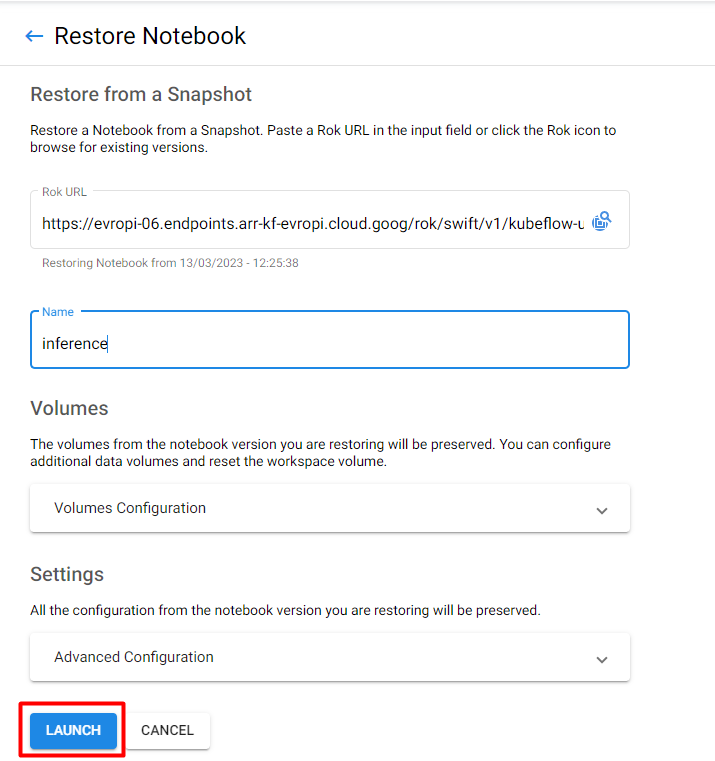
5. Create the notebook
Specify a name for your server, and click on LAUNCH:
2. Open the artifacts bucket
Click on the artifacts bucket:
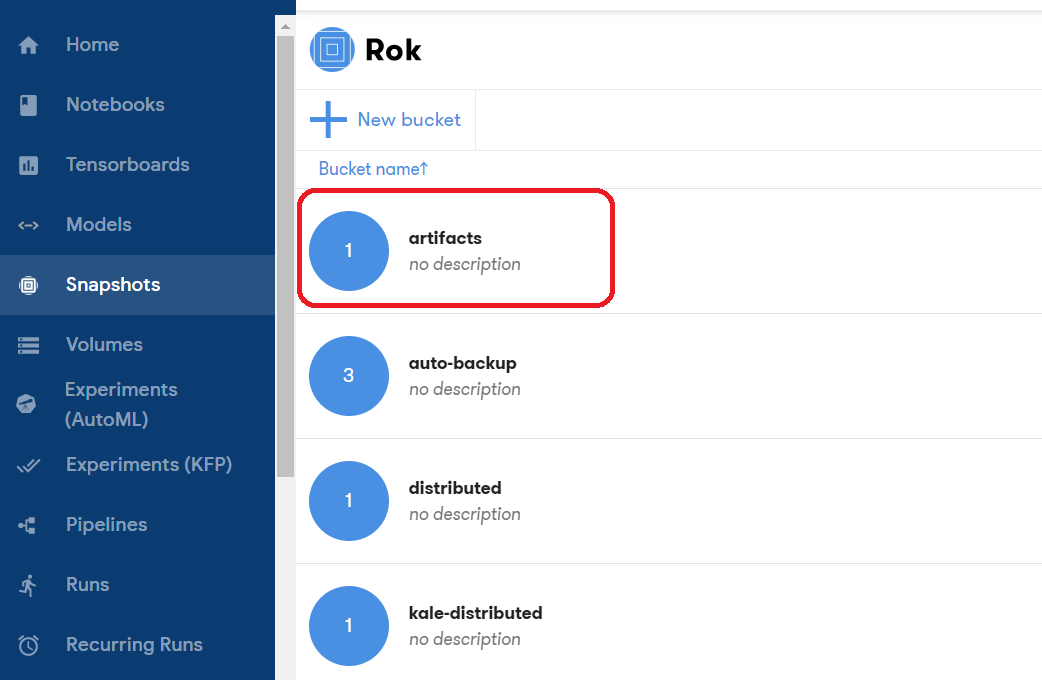
3. Choose the snapshot
There should be one entry inside it. If not, choose the most recent one based on the Created column:
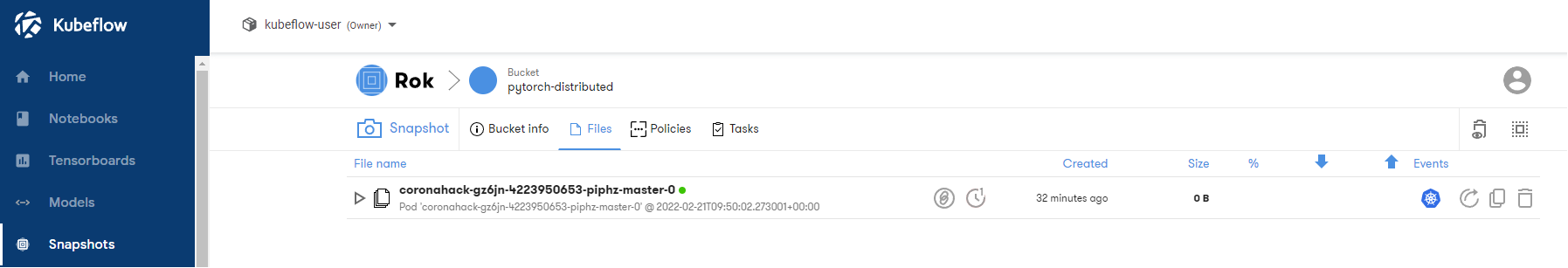
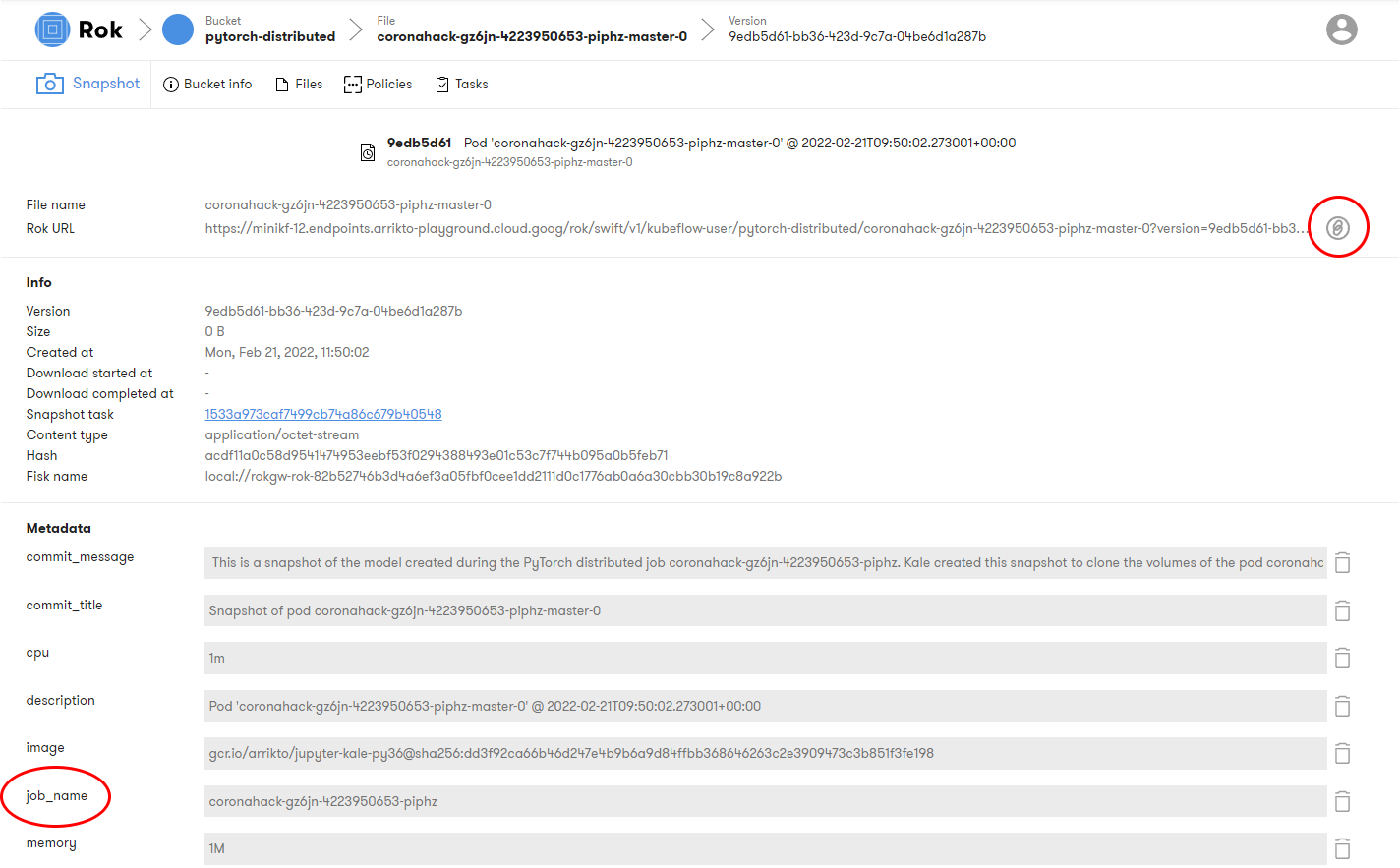
4. Copy the snapshot URL
Copy the Rok URL:
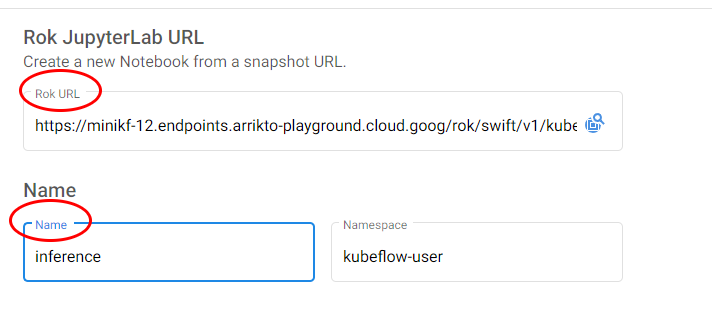
5. Create a new notebook
Go back to the Notebooks tab and create a new notebook. In the Rok URL field, paste the URL you copied in the previous step. Specify a name for the server, and hit the LAUNCH button:
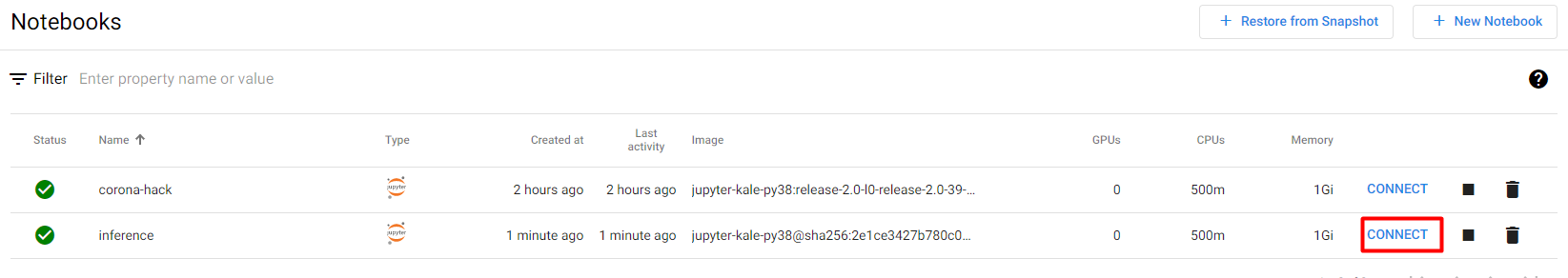
6. Connect to the notebook
When the notebook is ready, click CONNECT to connect to it:
7. Open the notebook file
In the sidebar, navigate to the folder examples/academy/coronahack-distributed-training/ and open the inference.ipynb notebook file:
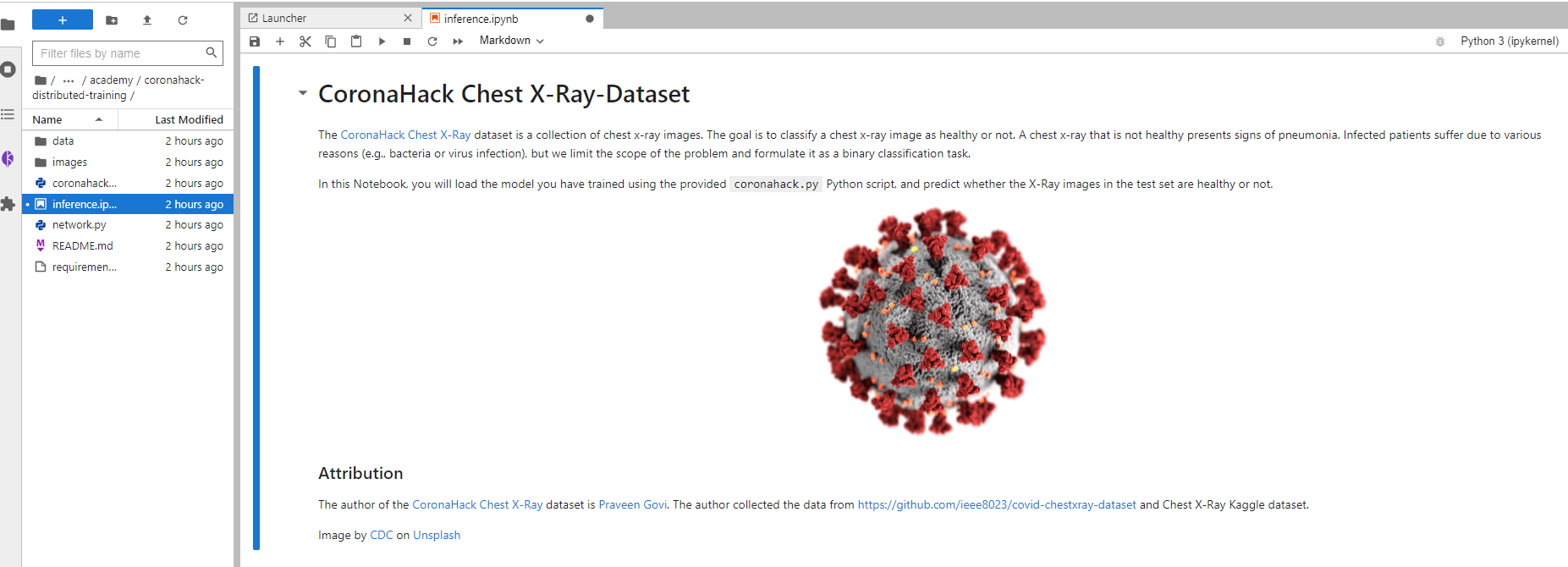
8. Run the cells
Now, go back to the beginning of the notebook and start running the cells one by one. You will first import some libraries:
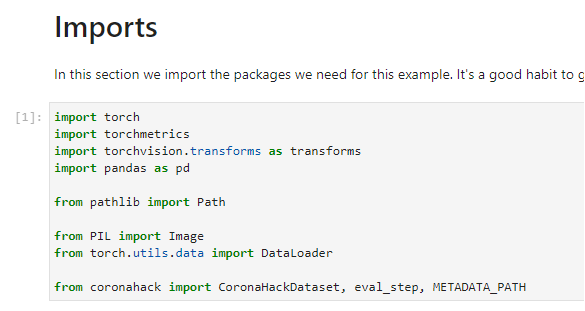
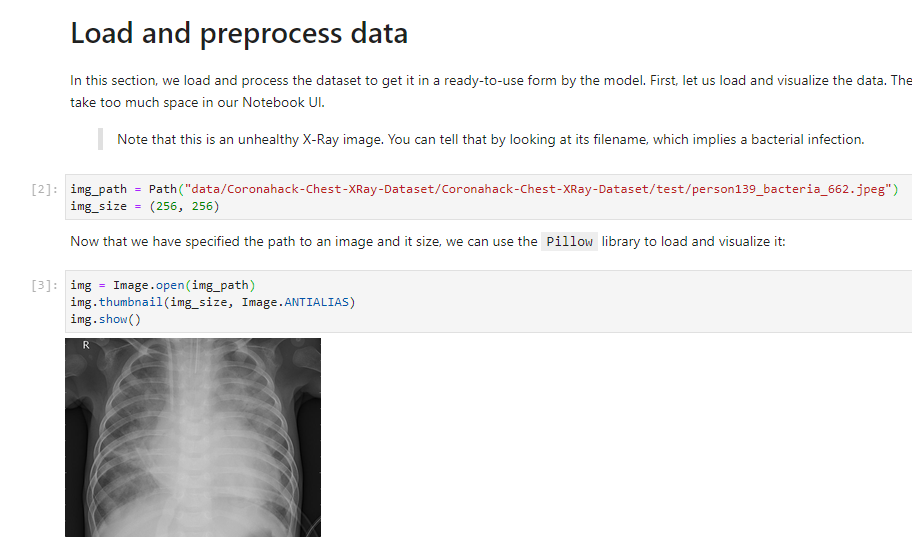
Then, you will load and preprocess the data:
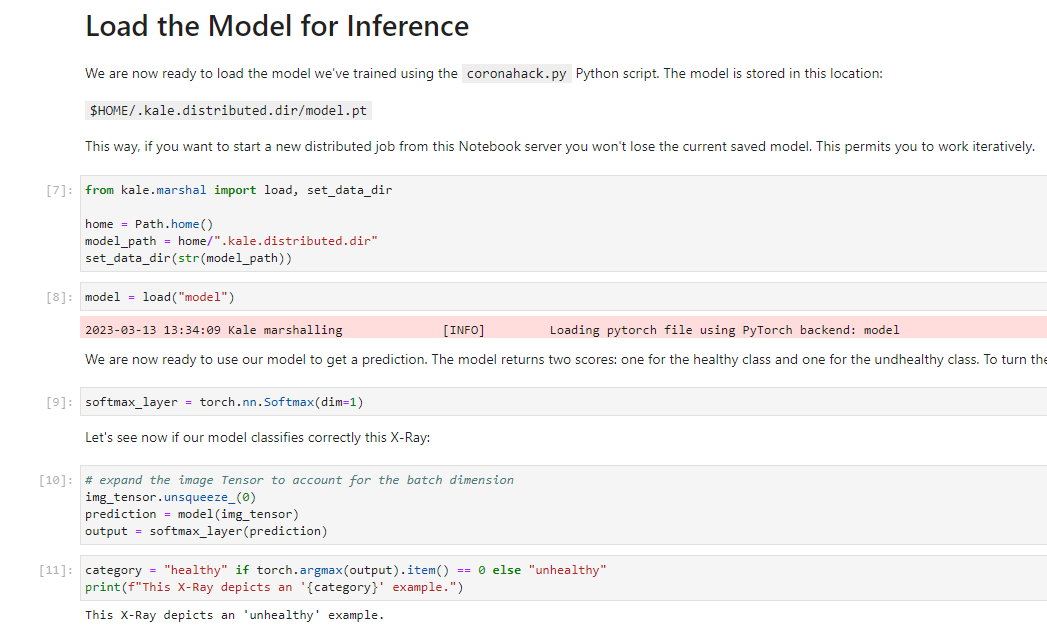
Load the model for inference:
Calculate the accuracy of the model using the test dataset:
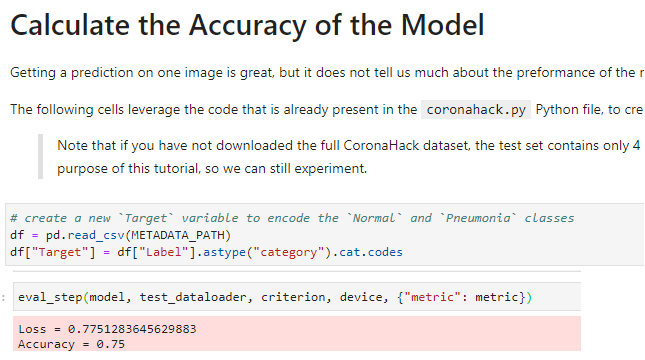
Congratulations! You loaded the trained model from the distributed process and used it to classify the images of the test dataset!